TYPES OF CELL WEBQUEST
CALIFORNIA STANDARD
CELL BIOLOGY
1.
The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of
chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism’s cells. As
a basis for understanding this concept:
c. Students know how prokaryotic
cells, eukaryotic cells (including those from plants and animals), differ in
complexity and general structure.
TASKS / OBJECTIVES:
1.
Know
the differences and similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
2.
Prokaryotic
cells:
a. Be able to draw and label the parts of a
prokaryote cell
b. Identify the parts of a prokaryotic cell
and know their functions
c. Give examples of prokaryotic cells
3.
Eukaryotic
cells:
a. Be able to draw and label the parts of an
ANIMAL eukaryote cell
i. Identify the organelles of an ANIMAL cell and know their functions
ii. Give examples of animal eukaryote cells
b. Be able to draw and label the parts of a
PLANT cell and know their functions
i. Identify the organelles of an PLANT
eukaryote cell
ii. Give examples of plant eukaryote cells
TIME FRAME: Three
days
MATERIALS: Your
textbook, Internet access, paper, writing tools, color pencils
INTRODUCTION:
Look at your hand
(yes, LOOK at your hand). Now, touch it (yes, TOUCH your hand). DO IT. Feel the
skin under your fingers… Have you EVER wonder…
1. What is the material that makes up my
skin called?
2. What is it made up of?
3. Why does it hurt or bleed when it is
injured?
4. Why does it heal and how does it happen?
5. How do I grow? How did I become the
person I am today from the embryo that grew up inside my mother’s womb?
The answers to all these
questions: CELLS
1. CELLS are the smallest units of LIFE that
make up living things.
2. ALL living things are made up of cells
3. UNICELLULAR organisms: 1 cell only
4. MULTICELLULAR organisms: more than 1 cell
(guess how many cells you have).
There
are two main types of cells: prokaryotes (very primitive and simple) and
eukaryote (more modern and complex).
Your
task is to develop an understanding of each one of these two types of cells J
PROKARYOTES versus
EUKARYOTES
1. What does “Karyose” mean and how does it
relate to PROKARYOTE and EUKARYOTE (give me their definitions)?
2. What is one very important difference
between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
3. LIST 5 similarities between prokaryotes
and eukaryotes
4. LIST 5 things that are different between
prokaryotes and eukaryotes
PROKARYOTES
Watch this video carefully before you start your assignment http://www.brainpop.com/science/cellularlifeandgenetics/cells/
Watch this video carefully before you start your assignment http://www.brainpop.com/science/cellularlifeandgenetics/cells/
1. Use one of the three sites above (or other of your
choice) to DRAW and LABEL a prokaryote cell:
a.
Label
the following: capsule, cell wall, cytoplasm, NUCLEOID (they don’t have
nucleus), plasma membrane, ribosomes, flagella, pili.
b.
LIST
their names and write their functions (what do they do?): capsule, cell wall,
cytoplasm, plasma membrane, ribosomes, flagella, pili,
2. Give me an example of a prokaryote cell
(look in your book or Internet).
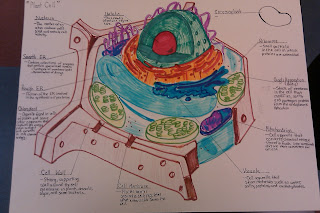
EUKARYOTES (ANIMAL CELLS)
1.
Use
one of these sites (or other of your choice) to DRAW and LABEL an animal eukaryote
cell:
a.
Label
the following: plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, nucleolus, rough endoplasmic
reticulum, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus (complex), ribosomes,
mitochondrion
b.
LIST
and write their functions (9 total)
EUKARYOTES (PLANT
CELLS)
1.
Use
one of these sites (or other of your choice) to DRAW and LABEL a plant
eukaryote cell:
a.
Label
the following: plasma membrane, cell wall cytoplasm, nucleus, nucleolus, rough
endoplasmic reticulum, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus (complex),
ribosomes, mitochondrion, chloroplast, vacuole.